If snoring wasn’t enough, science proves that there’s more done in the process of sleeping than just the creation of loud noises. Did you know that night shift workers tend to have more health and sleeping problems than non-shift workers? Did you know that there is such thing as being a “morning person” or a “night owl”? The National Sleep Foundation describes how our sleep patterns are based on our individual biological clocks which regulate our sleeping patterns. Here are seven other things you may not know about sleep:
1 Loud and frequent snoring during sleep is a distinguishable characteristic of sleep apnea, a disorder in which breathing is stopped for several seconds at frequent points in your sleep.
While absurd snoring can be just a laughable joke, the result of snoring can lead from anywhere to diabetes and heart problems to heart disease and even death. Sleep apnea can make you very sleepy everyday and can lower the oxygen levels in your blood if left untreated. No oxygen means no life can flourish in your body, including the livelihood of the cells in your brain, heart and other organs.
2 Constantly keeping yourself up at night to finish work and the alarm clock is set for 5 a.m.? Avoid it.
Self-imposed sleep deprivation can cause excessive sleepiness, a condition that makes it brutal to get out of bed in the morning and easy to fall asleep at the wheel of your car. A National Sleep Foundation study found that 36 percent of Americans drove drowsy or fell asleep while driving in 2008. Other sleepy side effects are narcolepsy, insomnia, snoring and restless leg syndrome (a neurological condition that causes painful tingling in the legs).
3 Extra sleep conserves and produces helpful hormones called cytokines that fight infection.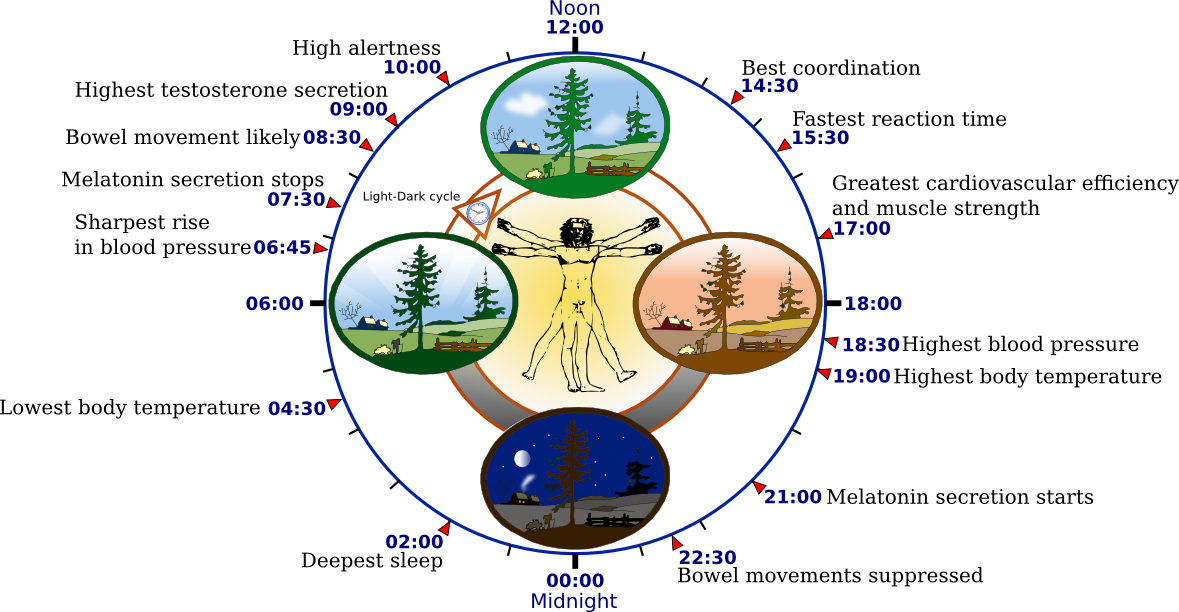
4 Sunlight, or the lack of it, can tell your body to sleep or stay awake.
Ever wonder why you tend to sleep between midnight and 7 a.m.? Darkness triggers melatonin, a natural hormone that makes you tired.
5 While lightness and darkness can hint to your body that it should sleep, your body is also a factor in making sure that the body knows it’s time to sleep.
From the moment you awaken, a natural chemical called adenosine builds in the blood stream. The more time you remain awake, the more adenosine is generated. It’s function: to make you sleepy.
6 Drinking excessive beer and liquor can disturb a good night’s sleep.
For instance, drinking more than what you can normally stand will either wake you up earlier than usual or make you come in and out of sleep.
7 The common saying “sleep on it, and get back to it later” is more scientifically-based than it sounds.
The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute reported that studies prove people learn better when well rested, and that memory improves with a good night’s sleep.
Information provided by the National Sleep Foundation and The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute.
__________________________
ATTRIBUTION:
Images
Biological Clock – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Biological_clock_human.PNG

